What Machine is Used to Make Underground Tunnels?
What Machine is Used to Make Underground Tunnels?
The creation of underground tunnels – arteries for transport, utilities, and exploration – is a marvel of modern engineering. When picturing the machines responsible for burrowing through rock and soil deep beneath our feet, colossal Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs) often dominate the imagination. While these mechanical behemoths are indeed the primary workhorses for large-scale tunnel excavation, the reality of tunnel construction involves a sophisticated ecosystem of specialized equipment. Among these, the versatile demolition robot plays an increasingly critical, though sometimes understated, role, particularly in precision tasks and challenging environments where brute force isn't enough.
The Undisputed Kings: Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs)
The answer to the titular question, for most major projects, is unequivocally the Tunnel Boring Machine. TBMs are engineering masterpieces designed for continuous, efficient, and relatively safe excavation in a wide range of ground conditions, from soft clay to hard rock.
How They Work: A TBM is essentially a mobile factory. At its cutting face, a rotating cutterhead, equipped with disc cutters (for rock) or cutting tools (for soil), chips away at the tunnel face. The excavated material (muck) is transported back through the machine via a conveyor system. Simultaneously, behind the cutterhead, the machine erects pre-cast concrete segments to form the tunnel lining, creating a stable structure immediately.
Types of TBMs:
Earth Pressure Balance Machines (EPBMs): Ideal for soft ground (clay, silt, sand). They use the excavated material itself, mixed with additives, to create a pressurized slurry at the face, balancing the earth pressure and preventing collapse.
Slurry Shield TBMs: Used in unstable ground, especially below the water table. They use a pressurized mixture of bentonite clay and water to support the tunnel face. The excavated material is mixed with this slurry and pumped to the surface for separation.
Hard Rock TBMs (Gripper TBMs): Designed for stable rock formations. They use grippers that brace against the tunnel walls to propel the machine forward. Disc cutters fracture the rock.
Dual Mode TBMs: Hybrid machines capable of switching between EPB and Slurry modes, or handling mixed ground conditions (rock and soil).
Advantages: High production rates, increased safety (minimizing worker exposure at the face), reduced ground settlement (critical in urban areas), and the ability to install the final lining concurrently.
Beyond the Bore: The Supporting Cast in Tunnel Construction
While the TBM does the primary excavation, tunnel construction is a complex symphony requiring numerous supporting machines:
Roadheaders: These are track-mounted or boom-mounted machines with a powerful cutting head (often a rotating drum with picks). They are highly maneuverable and excellent for smaller tunnels, irregular shapes, cross-passages, station caverns, or hard rock where a full-face TBM isn't feasible or economical. They excel at selective excavation.
Drill and Blast Equipment: The traditional method, still vital for hard rock tunnels, particularly in remote areas or complex geologies. Involves drilling precise blast holes, loading explosives, detonating, and then removing the fragmented rock (mucking) using loaders and dump trucks.
Microtunneling Machines: Remote-controlled, guided boring machines used for installing pipelines and small-diameter tunnels (typically 0.6m to 3m). They are launched from a pit, excavate the ground (often using a cutterhead and slurry system), and install pipe segments behind them as they advance.
Mucking Equipment: Crucial for removing excavated material. This includes conveyor systems (integral to TBMs), muck cars pulled by locomotives, shuttle cars, and heavy-duty dump trucks for drill-and-blast operations.
Lining Equipment: Besides the TBM's segment erector, this includes concrete spraying machines (shotcrete) for initial ground support in drill-and-blast tunnels or roadheader drives, and equipment for installing rock bolts and steel arches.
Where the Demolition Robot Excels: Precision in the Depths
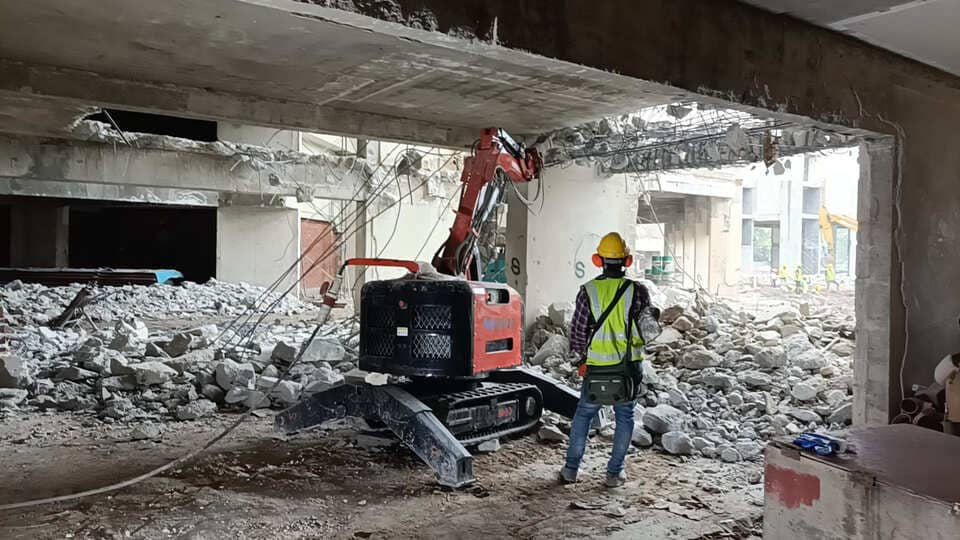
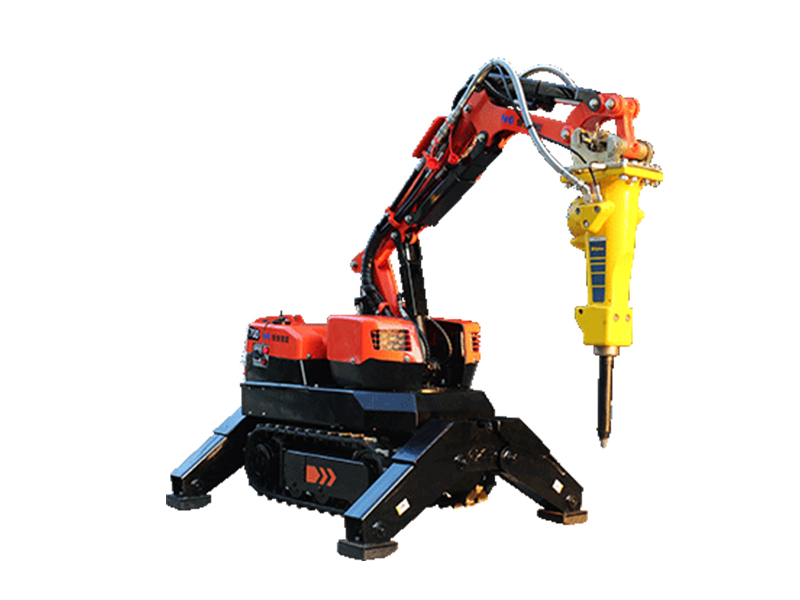
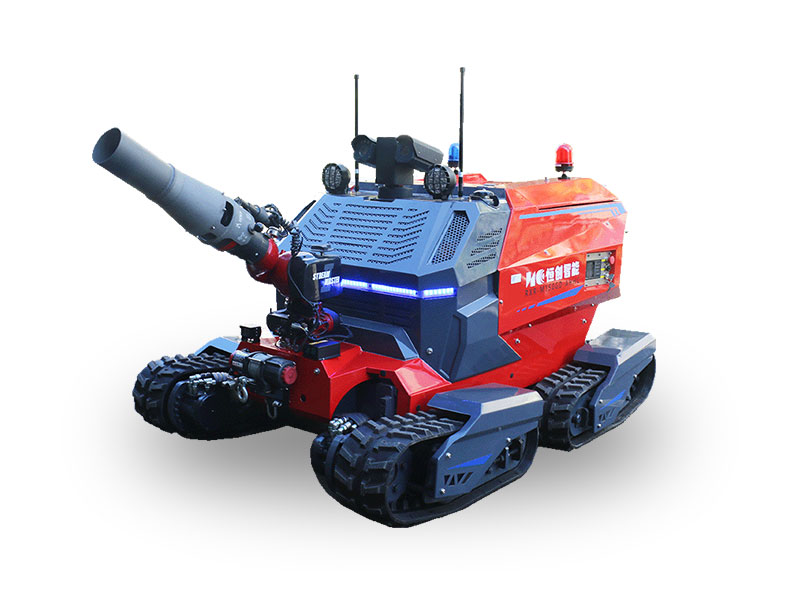
This is where the demolition robot steps into the spotlight within the tunnel construction ecosystem. While not an excavation machine per se, its role is indispensable for specific, high-precision tasks that larger machinery simply cannot handle effectively or safely:
Breaking Obstacles: TBMs can encounter unexpected obstacles – old foundations, boulders, or sections of exceptionally hard rock that challenge even disc cutters. Sending workers to manually break these with jackhammers is dangerous and slow. A demolition robot, equipped with a hydraulic breaker or crusher attachment, can be remotely operated to safely and efficiently break apart these obstacles directly at the tunnel face or within the TBM chamber.
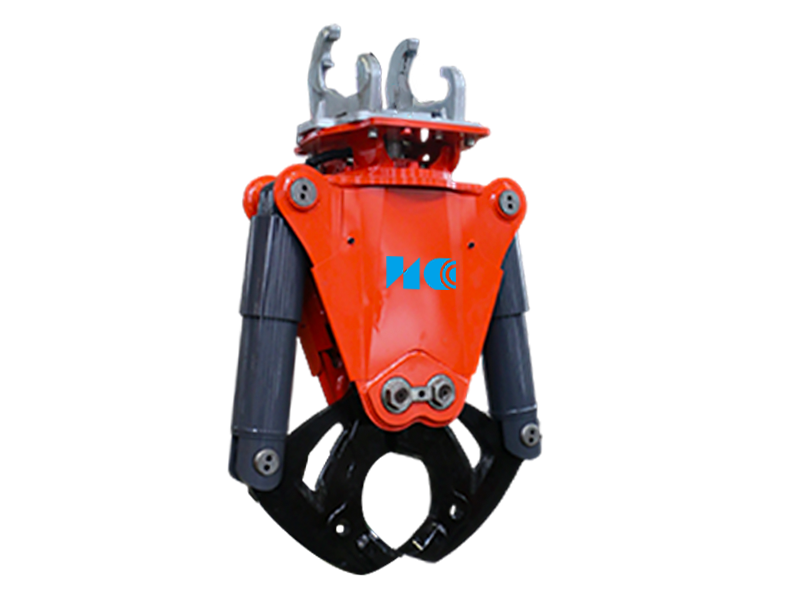
Precision Shaping & Scaling: After primary excavation (by TBM, roadheader, or blast), tunnel walls often require profiling and scaling – removing loose rock or overbreak to achieve the precise final profile needed for lining installation. Demolition robots, with their articulated booms and various attachments (breakers, crushers, buckets), offer unparalleled precision for this delicate work, minimizing damage to the surrounding rock mass.
Creating Openings and Cross-Passages: Excavating niches, cross-passages between tunnels, station entrances, or ventilation shafts off the main tunnel bore requires precision. Demolition robots are maneuverable enough to access these confined areas and perform controlled demolition and excavation without the vibration and overbreak risks associated with larger machinery or uncontrolled blasting.
Concrete Demolition & Rehabilitation: During tunnel maintenance, repair, or enlargement, sections of existing concrete lining may need removal. Demolition robots are perfect for this selective demolition, minimizing disruption and vibration to the surrounding structure.
Safety in Hazardous Zones: Working in confined spaces, near unstable ground, or after a TBM stoppage due to obstacles presents significant risks. Remote operation of a demolition robot keeps personnel out of harm's way, enhancing overall site safety.
Why Demolition Robots are Gaining Ground in Tunneling:
Enhanced Safety: Remote operation drastically reduces worker exposure to falling debris, dust, noise, and potential collapses at the tunnel face.
Unmatched Precision: Articulated arms allow for highly controlled breaking in tight spaces and complex geometries.
Reduced Vibration: Compared to large excavators using breakers, modern demolition robots generate significantly less vibration. This is crucial in urban environments to protect surface structures and existing underground infrastructure.
Increased Efficiency: Faster obstacle removal and precision work compared to manual methods minimize costly delays to the primary excavation process.
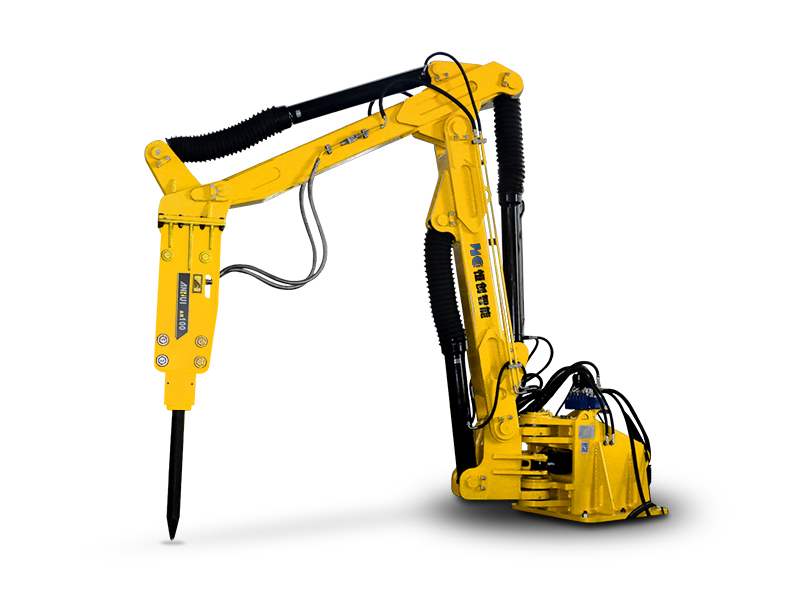
Versatility: A single demolition robot base unit can utilize multiple attachments (breakers, crushers, buckets, drills, scalers), making it adaptable to various tasks throughout the project lifecycle.
The Future of Tunnel Construction Machinery
Tunnel construction continues to evolve, driven by demands for safety, speed, cost-efficiency, and minimal environmental/social impact. TBMs are becoming more sophisticated, with advanced guidance systems, ground conditioning capabilities, and remote monitoring. Automation is increasing, from automated muck trains to robotic systems for segment handling and grouting.
The role of the demolition robot is also set to expand. Integration with real-time scanning (LiDAR) for precise mapping of surfaces to be broken, enhanced remote control systems with better situational awareness, and even semi-autonomous operation for repetitive tasks are on the horizon. Their ability to perform dangerous, precise work makes them an increasingly vital tool in the tunnel builder's arsenal.
Conclusion
So, what machine is used to make underground tunnels? The dominant answer remains the Tunnel Boring Machine, a triumph of engineering enabling the creation of vast subterranean networks. However, tunnel construction is a complex ballet, and the demolition robot has secured a starring role as the agile, precise, and safe solution for the intricate tasks that lie beyond the main bore. From clearing unexpected obstacles and profiling rough walls to creating vital connections and enabling safe repairs, these remotely operated powerhouses are proving indispensable allies to the titanic TBMs, ensuring that the challenging work of building beneath our world continues to advance with greater efficiency and safety than ever before.
FAQs: Machines for Underground Tunnels & Demolition Robots
Q: Is a demolition robot the main machine for digging large tunnels?A: No. Large tunnels are primarily excavated by Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs) or, in hard rock, sometimes by drill-and-blast methods or roadheaders. Demolition robots are used for specialized, precise tasks within the tunnel construction process, like breaking obstacles, scaling walls, or excavating cross-passages.
Q: What are the biggest advantages of using a demolition robot in a tunnel?A: The key advantages are enhanced safety (remote operation keeps workers out of hazardous zones), superior precision (articulated arms for controlled work in tight spaces), and reduced vibration (crucial for protecting nearby structures and infrastructure).
Q: Can demolition robots work in very small tunnels?A: Yes, a major strength of demolition robots is their compact size and maneuverability. They are specifically designed to operate effectively in confined spaces, making them ideal for smaller tunnels, cross-passages, niches, and repair work where larger equipment cannot fit.
Q: What attachments do demolition robots use in tunnels?A: Common attachments include hydraulic breakers (hammers) for fracturing hard material, crushers for pulverizing concrete or rock, buckets for light excavation and mucking, and sometimes specialized scalers or drills. The attachment is chosen based on the specific task.
Q: Are demolition robots replacing human workers in tunnels?A: Not replacing entirely, but significantly augmenting and making work safer. They take over the most dangerous tasks (like working at an unstable face or breaking obstacles near the cutterhead). Humans remain essential for operating, supervising, and maintaining the robots, as well as performing numerous other complex tasks throughout the construction process. Their use represents a shift towards safer and more efficient practices.
Read More